If you are looking wholesale lighting solutions, click here.

Do you want to upgrade your lighting system with a low-cost, energy-efficient solution? LED technology has altered the lighting business by providing greater brightness, longevity, and sustainability than traditional lighting.
In this article, we’ll look at the basics of LED lighting and learn about LED lighting selection. Let’s look at the science, applications, and breakthroughs influencing the future of lighting.
LED is short for light-emitting diodes. It is a semiconductor device that produces visible light. Light is produced when an electrical current is passed through it. The traditional incandescent bulbs the other hand, produce light by heating a filament.
LED produces light using electroluminescence. This technique turns electrical energy directly into light more efficiently than incandescent light. LED light bulbs work in the opposite way that photovoltaic cells do, converting light into power.
Instead, LEDs emit light by using electrical energy. Thus making them a highly efficient and cost-effective lighting solution. The various benefits of LEDs have led them to become the preferred choice for residential, commercial, and industrial lighting.

British scientist H.J. Round in 1907 discovered electroluminescence in silicon carbide. This discovery laid the groundwork for LED technology. However, practical applications went undiscovered until 1962.
When Nick Holonyak Jr. created the first red LED. This accomplishment signaled the start of solid-state lighting. Thus paving the path for broad innovation.
In the 1990s great work was done to advance high-power LEDs. Shuji Nakamura’s creation of blue LEDs made it possible to produce white LED lights.
Thus changing the lighting business. This discovery made it practical for general illumination. Hence resulting in their widespread adoption throughout industries.
LEDs were first restricted to indicator lights, electronic displays, and small-scale applications. This was due to their poor brightness and limited color possibilities.

However, with time, brightness, efficiency, and color rendering improved. Thus, LEDs evolved from specialized to mainstream lighting solutions in commercial, industrial, and residential settings.
Today, they are utilized in streetlights, automobiles, business buildings, and even smart homes.
Modern LED technology has advanced significantly, setting the norm for energy-efficient lighting. Major advancements in the LEDs used in lighting include:

These advancements established LED light bulbs as the premier alternative for long-lasting, high-performance lighting.
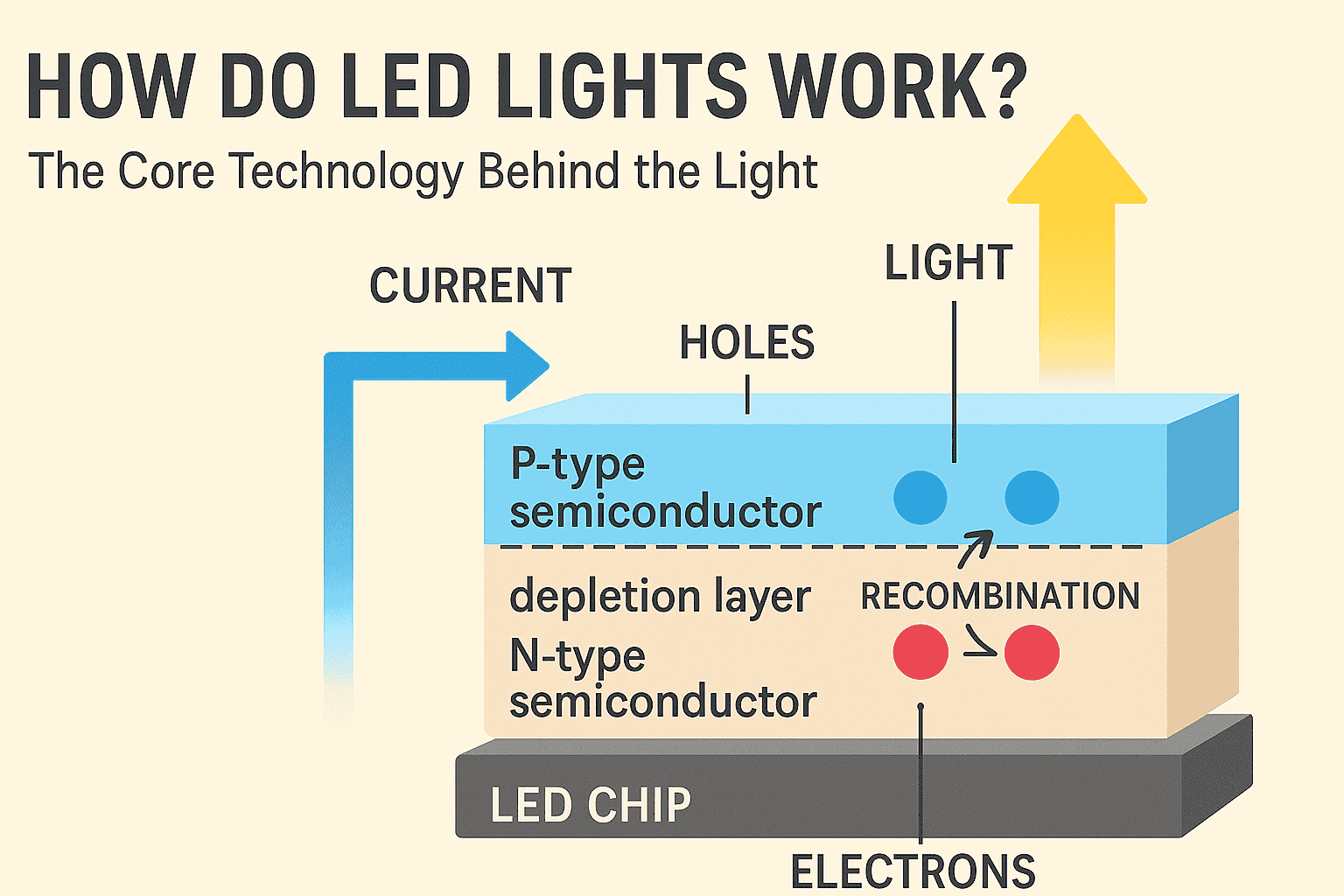
LEDs work on the principle of electroluminescence, which is the conversion of electrical energy into light. LED light bulbs generate light directly from a semiconductor.
Unlike incandescent bulbs, which rely on heated filaments. And fluorescent lights, which employ gases and mercury vapor. This novel approach makes LEDs substantially more energy-efficient and durable.
Every LED contains a semiconductor chip. This chip is commonly comprised of gallium nitride (GaN) or other compound semiconductors.
When an electric current flows through the LED, it excites electrons within the material, causing them to change energy levels. This movement provides light while producing very little heat loss. Thus making LED bulbs extremely efficient.
Imagine a waterfall: electrons are like the water drops at the top (high energy state). When they fall, they emit energy. However, in LEDs, this energy is released as light rather than heat.
An LED contains two layers of semiconductor material:
When an electrical current is provided, electrons transfer from the N-type layer to the P-type layer. As electrons fill these “holes,” they emit energy in the form of photons.
The result is the visible light spectrum. The lighting products are defined differently based on the semiconductor materials. You can opt for an LED that physically resembles familiar light.
Unlike incandescent bulbs, LEDs can be configured to provide a wide range of color temperatures. These include warm white (2700K) and cool daylight (6500K).
This is accomplished by changing the semiconductor composition. It can also be done by using phosphor material coatings to alter the radiated wavelengths.
Furthermore, LEDs are far more energy-efficient than traditional lights. They convert approximately 90% of the energy into visible light. On the other hand, incandescent bulbs release 90 percent energy as heat.
This efficiency translates into lower electricity usage and a longer lifespan. This makes LEDs an excellent choice for both household and commercial lighting applications.
The proper LED lighting depends on your specific requirements. Whether for small gadgets, commercial settings, or industrial applications. Here we’ve broken down the most common forms of LED technology and their applications.

Standard LEDs are the most basic sort of light-emitting diode, and they are widely used in small-scale devices. They are employed as indicator lights in appliances, digital displays, and signage.
Because of their low power consumption and small size, they are perfect for applications that require a small amount of light.
Surface-mounted device (SMD) LEDs are popular due to their great brightness. They also have a small construction. These LEDs are directly installed on a circuit board, making them perfect for use in LED strips, retail lighting, and backlit displays.
Their versatility and energy efficiency make them a popular choice for both decorative and functional lighting.

Chip-on-board (COB) LEDs are designed for high-intensity illumination and provide more light in a small space. They are often utilized in warehouses, factories, and big commercial environments.
These places require bright, homogeneous lighting. Their great efficiency and ability to eliminate glare make them ideal for industrial and high-performance applications.
Efficiency: SMD and COB LEDs produce more lumens per watt than conventional diodes.
Cost-effectiveness: Standard diodes are the least expensive. Whereas COB LEDs have a higher initial cost but provide greater light.
Size and application: Standard diodes are ideal for small-scale applications. SMDs for flexible and decorative lighting, and COBs for high-intensity commercial lighting.
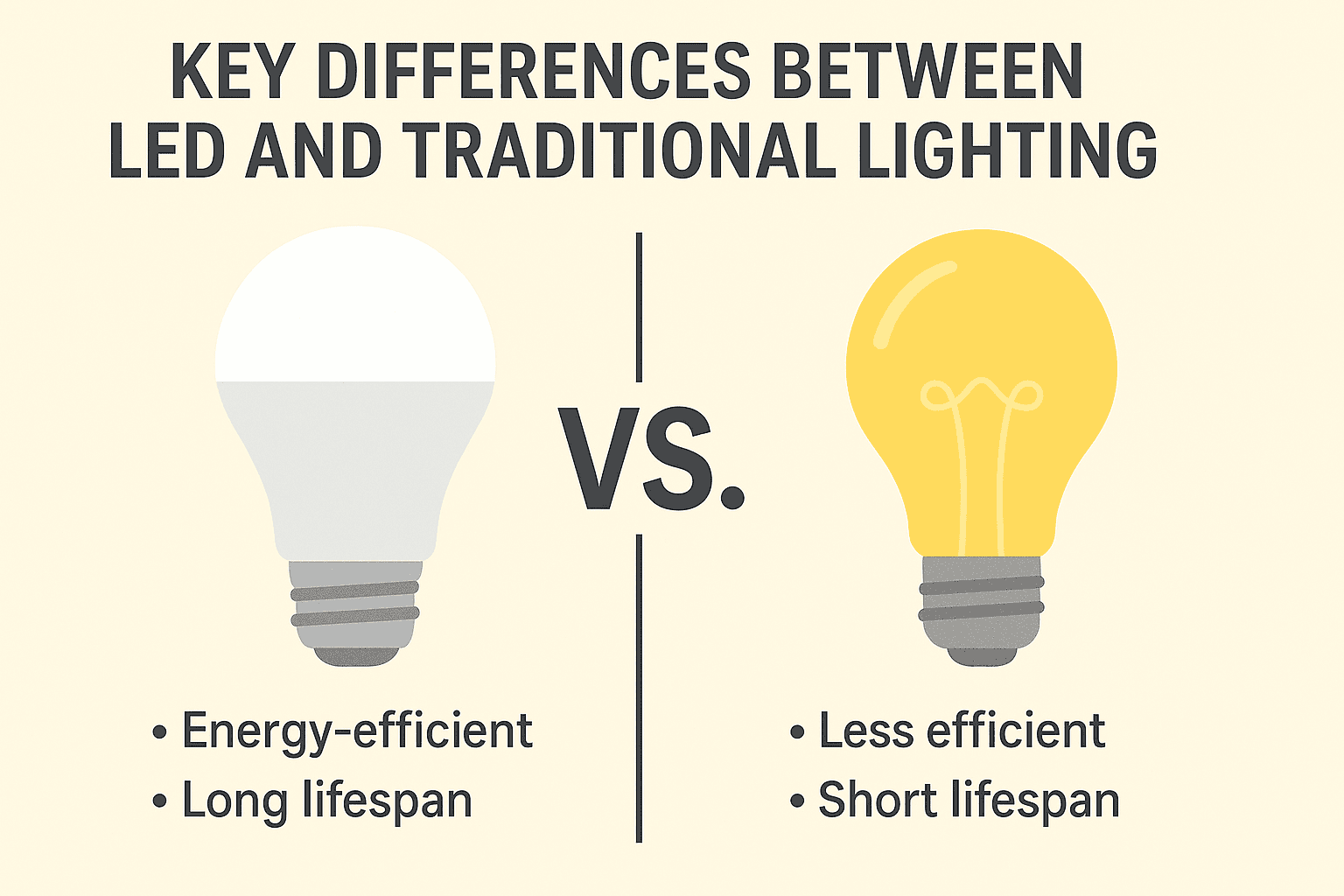
LED technology has transformed the lighting business. By providing energy-efficient, long-lasting, and focused lighting options. LEDs use less energy and give superior illumination. Unlike classic incandescent or compact fluorescent CFL.
One of the key advantages of LEDs is their directional lighting capability. Unlike typical light bulbs, which emit light and heat in all directions, LEDs focus light in a specific direction, reducing light loss and increasing efficiency.
This makes them excellent for task lighting, spotlights, and industrial applications requiring precision illumination.
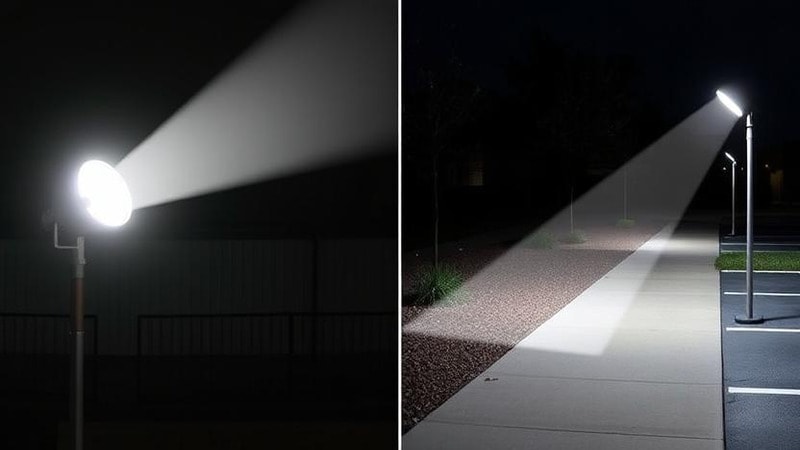

LEDs consume far less energy than incandescent lamps while generating the same or better brightness. LEDs turn the vast majority of their energy directly into visible light.
LEDs’ efficiency allows them to last up to 25 times longer than incandescent bulbs and three to five times longer than compact fluorescent lighting CFLs, resulting in decreased replacement and maintenance costs.
LEDs create white light by combining multiple colored LEDs (red, green, and blue) into a recognizable white hue. This method gives you more flexibility over color temperature, allowing for warm, cool, and daylight changes.
| Feature | LED Lighting | Incandescent Bulbs | CFL (Compact Fluorescent) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Uses 80-90% less energy | Least efficient, wastes 90% as heat | More efficient than incandescent but less than LEDs |
| Lifespan | 25,000 - 50,000 hours | 750 - 2,000 hours | 8,000 - 15,000 hours |
| Heat Emission | Minimal heat production | Very high heat emission | Moderate heat emission |
| Brightness | Instant full brightness | Instant full brightness | Takes time to warm up |
| Durability | Shock-resistant, solid-state | Fragile, glass filament | Fragile, glass tubing |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, no mercury | High energy waste | Contains mercury, requires special disposal |
| Upfront Cost | Higher initial cost, but long-term savings | Low initial cost, frequent replacements needed | Moderate cost, but less durable than LEDs |
Fluorescent lighting is a popular choice for workplaces, warehouses, and commercial facilities due to its energy efficiency and affordability. The light output of fluorescent bulbs is controlled by phosphor coatings within the tube.
The phosphor-electricity reaction generates ultraviolet UV light. Which is then converted into visible light. This procedure uses multiple color temperatures, measured in Kelvin (K), to produce a distinct shade of white light.
Fluorescent lights are often divided into three color ranges: warm white (2700K-3000K), cool white (3500K-4100K), and daylight (5000K-6500K).
While these give useful lighting alternatives, the color accuracy and consistency could decrease over time owing to phosphor degradation, resulting in flickering or fading.

Furthermore, fluorescent bulbs lack accurate color control, making them less suited to modern lighting requirements.
LEDs provide remarkable color versatility due to their semiconductor-based construction. Instead of relying solely on phosphor coatings, LEDs achieve a wide range of colors by emitting light directly from various semiconductor materials or using phosphor conversion processes to produce white light.
This provides steady, high-quality illumination that is stable throughout time. One of the most significant advantages of LED technology is its ability to create a diverse spectrum of colors, including RGB (Red, Green, Blue) possibilities.
RGB LEDs are great for ambient, dynamic, and decorative lighting applications because they can create millions of color combinations by combining primary colors, unlike fluorescents, which are only able to produce preset color temperatures.
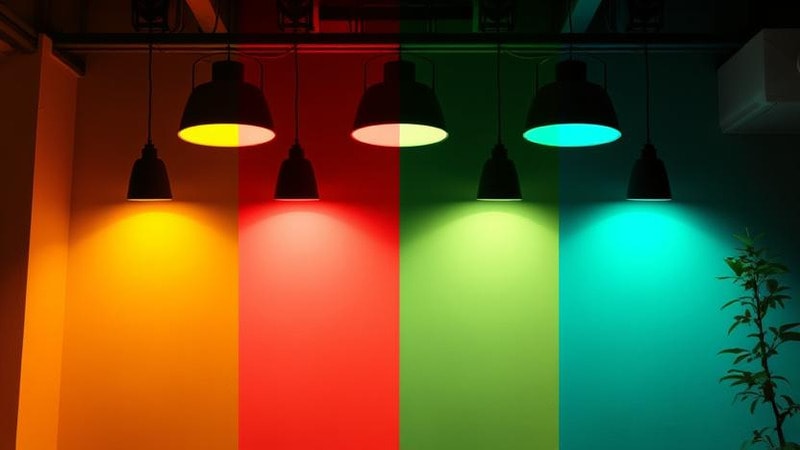

Furthermore, LEDs are smart lighting compatible, allowing users to control brightness, alter colors, and program lighting effects via remote controllers or mobile apps.
It is extremely important to choose the right lighting for your project. The shade, angle, and type of light dispersion can have a significant impact on the final look of the space.
These factors also impact the functionality and appeal of the project. Here is how to choose the right LED lighting for your project.
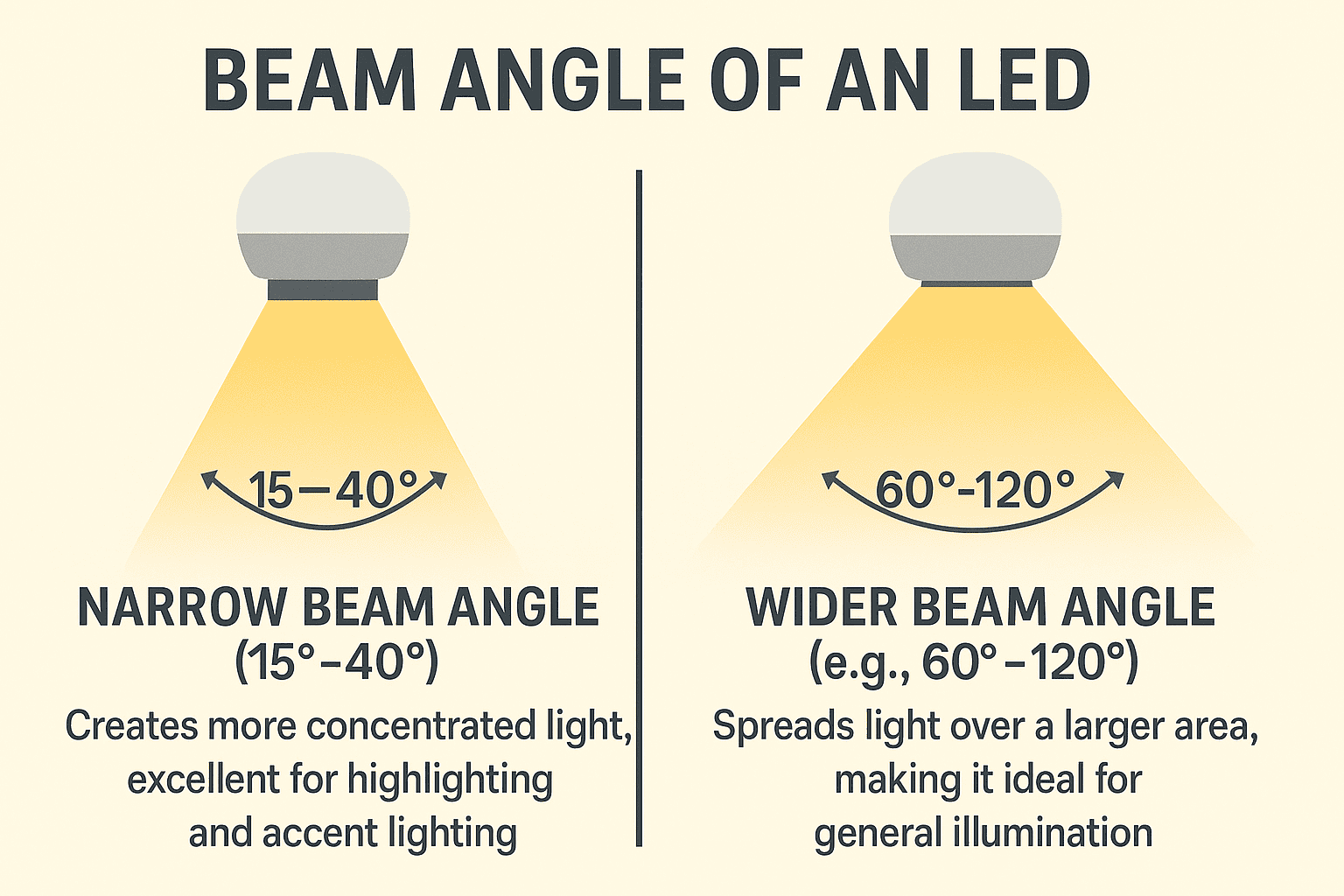
The beam angle of an LED controls how widely or narrowly it distributes light. A narrow beam angle (15°-40°) creates more concentrated light, making it excellent for highlighting and accent lighting in retail displays or art galleries.
A wider beam angle (e.g., 60°-120°) spreads light over a larger area, making it ideal for general illumination in offices, warehouses, and big commercial buildings.
Choosing the proper beam angle is critical for maximizing visibility, decreasing glare, and improving the overall vibe of an area.
Proper lighting distribution is necessary for both aesthetics and functionality. Uneven illumination can create shadows, hotspots, and dark zones, affecting vision and comfort. LEDs are intended to provide consistent light dispersion.
Choosing LEDs with diffused lenses or reflectors helps to maintain uniform light levels throughout a space, reducing eye strain and increasing productivity in work settings.
A light source’s ability to create colors in comparison to natural daylight is measured by the Color Rendering Index (CRI). LEDs with a CRI of 80 or above are best suited for workplaces, homes, and general applications.
Whereas CRIs of 90 or more are suitable for retail establishments, photography studios, art galleries, and medical facilities where color accuracy is essential.
A high CRI guarantees that colors appear vibrant and true to life, making products more appealing in retail settings and boosting visual clarity in offices.

LED lighting’s long lifespan and low energy consumption are two of its biggest benefits. LEDs significantly reduce electricity costs by using up to 80% less energy than conventional lighting.
Businesses can assess their return on investment (ROI) by comparing upfront LED installation expenses to long-term energy savings.
Furthermore, several government incentives and rebates encourage businesses to adopt energy-efficient lighting solutions, which increases cost-effectiveness.
Invest in high-quality products by buying from a company that has received the ENERGY STAR certification. These items undergo extensive testing to guarantee that they fulfill efficiency, brightness, and performance specifications. ENERGY STAR-certified bulb LEDs.

Choosing ENERGY STAR-certified LEDs allows you to minimize your carbon footprint, save power bills, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
LED technology has changed the lighting business by providing unparalleled energy efficiency, durability, and diversity. LEDs are a cost-effective and sustainable lighting solution.
They can be used for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. They are capable of lowering energy usage and maintenance expenses. Their adjustable color temperatures and improved light quality make them the favored option for modern lighting applications.
As a reputable manufacturer with more than 15 years of expertise. Risun Corp specializes in cutting-edge LED solutions that improve efficiency and performance.
Our high-quality LED products meet industry requirements and give long-term value to organizations, businesses, and wholesalers across multiple industries.
Are you looking to update your lighting system? Schedule a free consultation to find the ideal lighting solution for your requirements!
A. LEDs utilize up to 80% less energy and last much longer than incandescent bulbs. Thereby lowering electricity bills and maintenance costs.
A. There are many different types of LEDs, such as COB LEDs, SMD LEDs, and ordinary diodes. Each is designed for a specific application such as accent lighting, retail displays, and industrial use.
A. Yes, weather-resistant and waterproof LEDs are available for outdoor applications. They can be used in streetlights, security lighting, and landscape lighting.
A. No, LEDs do not emit UV light or radiation or excessive heat. Thus making them safer than traditional lighting. Choosing warm or neutral color temperatures can also help alleviate eye strain.
A. You have to consider factors such as beam angle, color temperature, CRI, and lumens. These considerations ensure that the LED light fits your aesthetic and practical requirements.
Comprehensive Lighting Solutions for MRO Wholesalers and Professionals
send your inquiry
Hi, I'm the author of this post, and I have been in this field for more than 15 years. If you want to wholesale lighting fixtures or lighting related product, feel free to ask me any questions.
Learn More >>Download our catalog to view all of our lighting products.
Ready to get started ?
Send Your InquiryOur team will get back to you promptly

please
download
Get notified about new products
Our team will get back to you promptly!
Add your first comment to this post