If you are looking wholesale lighting solutions, click here.

Light bulbs, the brilliant inventions that have illuminated our world for centuries, are everyday objects we often take for granted. Yet, the process of their creation is a fascinating journey of science and innovation.
But how do these simple objects transform electricity into light, and what goes into their manufacturing process? In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating journey from raw materials to finished light bulbs. Let’s get started.
To understand how light bulbs are manufactured, it’s important to look at their history. Let’s head back to the 19th century. It was when gas lamps and candles were the norm, and the concept of electric light was just a twinkle in some inventors’ eyes.
Contrary to popular belief, Thomas Edison isn’t the sole genius behind the light bulb. While he indisputably played a crucial role in its development, he was building on the work of many others who had laid the groundwork.
In 1800, Sir Humphry Davy invented the first electric light, the Arc Lamp. However, it was too bright for domestic use and impractical as it didn’t last long. Through the mid-19th century, several inventors tinkered and toyed with designs, but it was Sir Hiram Maxim who first patented the incandescent lamp in 1878.
Thomas Edison developed a more practical and long-lasting bulb in 1879. It uses a lower current electricity, a small carbonized filament, and an improved vacuum inside the globe. That’s right, the game-changer was a better vacuum that prevented the filament from oxidizing and breaking too soon.
We’ve come a long way from Edison’s original design, with light bulbs now available to suit every conceivable need and preference. Whether you’re looking for energy efficiency, a particular color temperature, or even smart bulb functionality, there’s a type of light bulb out there just for you.
Below are the main types of light bulbs available today:
Incandescent bulbs are the classic, old-school kind of light bulbs. They’ve been around since Edison’s time and work by passing electricity through a wire filament until it gets so hot that it glows.
While these light bulbs might not be the most energy-efficient option, they still win points for their warm, inviting glow and are usually cheaper upfront. However, their lifespan is shorter than other bulbs and may cost you more in the long run.

CFLs are the curly-whirly ones you often see in stores. Compact fluorescent bulbs are pretty cool because they use a fraction of the energy of the old-school incandescent bulbs, saving you money on your electricity bills.
However, CFLs have a downside too. They take some time to warm up and reach their full brightness. And let’s not forget, they contain a small amount of mercury, so you must be careful if one breaks and when you’re disposing of them. Despite this, they’re a pretty good choice for many homes.
LED (Light Emitting Diodes) bulbs are the latest and greatest in light bulb technology. They use even less energy than CFLs, last longer, and don’t contain any hazardous materials like mercury.
They pass a current through a semiconductor material, illuminating the tiny light sources we call LEDs. This process, called electroluminescence, gives LED bulbs their signature cool-to-the-touch operation.
Unlike their incandescent and CFL siblings, LED bulbs don’t “burn out” in the traditional sense. Instead, they experience “lumen depreciation,” meaning they gradually grow dimmer over time but continue to provide usable light for a significantly extended period.
They’re a bit pricier upfront, but they quickly pay for themselves with their superior energy efficiency and lifespan, often lasting up to 10 years or more!

Halogen glass bulbs are like the close relatives of incandescent bulbs, with a little bit of added science that makes them more efficient. They operate on the same principle – electricity heats a tungsten filament until it glows, providing that familiar warmth of light we all know and love.
But here’s the twist: the bulb is filled with a halogen gas, which creates a chemical reaction that redeposits the evaporated tungsten back onto the filament.
Although halogen bulbs are more efficient than their incandescent counterparts, they still can’t hold a candle to the energy savings offered by CFLs and LEDs. They produce a lot of heat and have a relatively short lifespan, often around 2 to 3 years.

The raw materials used in bulb manufacturing can vary depending on the type of bulb (incandescent, fluorescent, LED, etc.).

Below are the most common types of glass components that make up a light bulb:
The glass outline holds all the other components of the bulb together and protects them from external factors. It is usually made of thin, heat-resistant glass that can withstand high temperatures.
The gas inside the bulb helps prevent oxidation of the filament. Different types of gases are used in bulbs, such as argon or nitrogen in incandescent bulbs and mercury vapor in CFLs.
The tungsten filament is the thin wire that heats up and produces light. It is made of a highly conductive and heat-resistant metal called tungsten, with a melting point of 3,410 degrees Celsius!
Contact wires are used to connect the filament to the other components of the bulb. They are usually made of highly conductive metals, or copper or nickel.
Support wires hold the filament in place and provide structural support for the bulb. Unlike contact wires, they do not transmit electricity and are often made of steel.
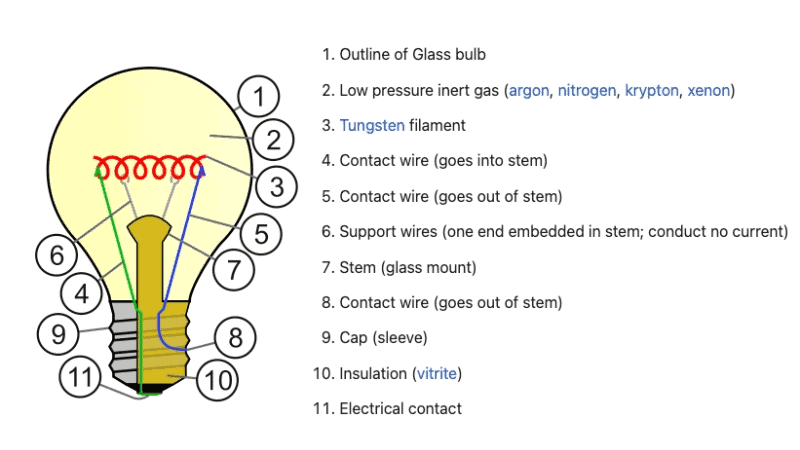
The stem is responsible for holding all the other components together. It is typically made of glass and connects all the wires and contacts.
The cap, also known as the sleeve, connects the bulb to a socket. It usually has screw threads or pins for insertion into a socket.
Insulation helps to protect against electrical shock by covering any live components inside the bulb. It is usually made of a ceramic material called vitrite.
The electrical contact connects the bulb to its power source, such as a light fixture or lamp. It can be made of different materials, including copper, aluminum, or silver-plated brass.
Making light bulbs combines precision engineering, careful selection of materials, and advanced manufacturing techniques. Here are the basic steps involved in making light bulbs:
Creating a light bulb starts with designing a blueprint, a map, for our tiny beacon of light. The blueprint maps out the bulb’s dimensions and features, defining aspects like the size of the glass envelope, the thickness of the filament, or the composition of the gas within.
Designing a blueprint is an intricate process, with engineers and designers working together, employing a mix of scientific knowledge, creativity, and innovation. They consider factors such as the bulb’s intended use, required lifespan, energy efficiency, and the cost of production.
Once the blueprint is all set, the next step is to gather the materials necessary for the light bulb production. As discussed above, the raw materials can range from glass for the bulb envelope to tungsten for the filament and even different types of gas.
Each material plays a specific role in making our bulb light up, last longer, and be energy efficient.

Procurement of these raw materials is a task in itself. Supplies are sourced from different parts of the world, ensuring the ideal combination of cost-efficiency and quality.
For instance, tungsten might be procured from China, the largest metal producer, while high-quality glass might come from Europe, known for its long history of glass manufacturing.
Now, onto the heart of the matter – the formation of the tungsten filament. This is where the magic starts to happen! This tiny, thin wire is responsible for all our bulb’s light. Can you imagine that? A small piece of wire illuminating entire rooms!
The process starts with raw tungsten, a silver-colored metal. This tungsten is converted into a fine wire, thinner than a human hair. Remember, we’re dealing with metal here. Tungsten has a super high melting point, perfect for emitting visible light without melting.
The tungsten wire is produced through heating, stretching, and coiling. It’s meticulously done to ensure the wire has the right thickness and length. The heating part is particularly interesting. The tungsten is heated to an incredible temperature until it almost becomes liquid. It’s then carefully stretched out to make the wire extremely fine and fragile.
Once we have our thin wire, we will coil it. Coiling increases its resistance to electricity, which is exactly what we need to get light from our bulb. The thin wire is wound around a molybdenum wire to create the coiled tungsten filament.
This is where our little light source starts to take shape! The process begins with high-quality heat-resistant glass. This glass is not ordinary; it’s designed to handle the high temperatures generated by the tungsten filament without cracking or melting.
Now, onto the fun part. The glass is heated until it’s molten – we’re talking a blazing 1,600 degrees Celsius here. Once in this state, it’s blow-molded into the bulb’s shape.
This process is fascinating to watch. The molten glass is captured on the end of a blowpipe, and a burst of air is blown into it, forming the bulb shape. It’s like watching a glassblower at work but on an industrial scale.

Once the shape is formed, it’s cooled down gradually in a process known as annealing. This is super important because it relieves any internal stresses in the glass that could cause it to shatter.
We’ve got all our pieces; now it’s time for the showdown – the assembly. This is where our glass bulb meets its shining heart, the tungsten filament, and everything else that makes it a functioning light bulb.
First off, the filament and support wires are assembled onto the stem. This delicate operation fits the filament into place just right so it can glow brightly without mishaps. We can’t have our filament flopping around, now can we?

Once that’s done, we turn our attention to the gas fill. Now, you might be wondering, why do we need gas in there? Well, it’s to stop the filament from burning out too quickly.
The gas, often argon or nitrogen, is pumped into the bulb to replace the air. This creates the perfect environment for our filament, helping it shine brighter and longer.
Next, we’ve got to attach the base to our little beacon of light. This part connects the bulb to the power source, like your favorite reading lamp. The base is usually made of metal – often brass or aluminum. It’s attached to the bottom of the light bulb and is insulated to prevent any electric shock.
Once the base is securely attached, it’s time to seal the bulb. This is a super important part of the process because it keeps the gas in and the air out.
Remember, filament loves that gas. It helps it burn brighter and last longer. The bulb is heated up and sealed off, locking the gas inside, and we have a working light bulb.

Let’s talk about the inner workings of our light bulb. How does it produce that cozy glow that brings your room to life? The magic happens when an electrical current passes through the tungsten filament.
As the filament resists the flow of electricity, it heats up to an incredible temperature, around 2,500 degrees Celsius. This heat causes the filament to glow white hot, and that’s the light you see emanating from your bulb.
So, let’s recap: electricity comes in, heats the filament, which glows bright, and voila, the room is illuminated!
Remember the gas we talked about that’s sealed inside the bulb? It also plays a crucial role. It slows down the evaporation of the tungsten filament, preventing it from burning out quickly and thus extending the life of your bulb.
So, the next time you flick on a light switch, take a moment to appreciate the brilliant science and intricate manufacturing process that brings a simple light bulb to life.

LED (Light Emitting Diode) bulbs are increasingly becoming the go-to choice for businesses around the globe. But what makes these little powerhouses of light such an attractive option?
LED bulbs are incredibly energy efficient. They use up to 80% less energy than traditional incandescent light bulbs. That’s a huge saving! Imagine what that could do to your electricity bills. Not only are you saving money, but you’re also doing your bit for the environment.
And let’s not forget about their longevity. LED bulbs do take the crown when it comes to lifespan. They can last up to 50,000 hours. Compare that to the 1,000 hours of an incandescent light bulb. Less frequent replacements mean reduced maintenance costs and less hassle for you.
Ever noticed how some lights take a bit of time to reach their full brightness? Not LED bulbs! These little wonders provide full brightness the moment they’re switched on. That’s instant light right when you need it, with no waiting around.
LED bulbs also operate at much cooler temperatures than other light bulbs. They are less likely to cause a fire and can reduce air conditioning costs in the summer months.
So, if you’re a business owner looking to cut costs, improve efficiency, and be a little kinder to the environment, LED bulbs are a bright idea!
In the future, we can anticipate a surge in the adoption of smart lighting technologies. IoT-integrated lighting solutions are paving the way for advancements such as customized lighting solutions, energy reporting, and automated energy-saving modes.
In addition, the field of Li-Fi (Light Fidelity) – a high-speed, bidirectional, and fully networked wireless communication technology using light – is also gaining traction. It uses light bulbs to transmit data, offering a more secure and efficient alternative to Wi-Fi.
Moreover, the rise of bio-adaptive lighting, which adjusts according to our biological and emotional needs, will revolutionize how we perceive and use light. Therefore, the future of lighting is likely to be a blend of intelligent, efficient, and responsive solutions.
Light bulbs have come a long way since the days of candles and oil lamps. From the invention of incandescent light bulbs to modern LED technologies, they continue to evolve and improve, illuminating our lives in more ways than one.
With advancements in efficiency, lifespan, and technology, who knows what bright ideas are yet to come?
Businesses worldwide are switching to energy-efficient lighting solutions, saving money and reducing their carbon footprint. Consider switching to LED bulbs if you want to upgrade your lighting and contribute to a greener future.
At Risun, we have a wide range of LED lighting solutions for businesses around the globe. Our products are designed for efficiency, durability, and environmental sustainability. Contact us today to learn more about our lighting solutions and join the revolution of energy-efficient lighting.
Comprehensive Lighting Solutions for MRO Wholesalers and Professionals
send your inquiry
Hi, I'm the author of this post, and I have been in this field for more than 15 years. If you want to wholesale lighting fixtures or lighting related product, feel free to ask me any questions.
Learn More >>Download our catalog to view all of our lighting products.
Ready to get started ?
Send Your InquiryOur team will get back to you promptly

please
download
Get notified about new products
Our team will get back to you promptly!
Add your first comment to this post